Frequently Asked Questions
1. What is the difference between mineral, ore and rock?
Minerals are naturally occurring inorganic solids with a crystalline structure and a definite range of chemical formula. Ores are concentrations of minerals in rock that are high enough to be economically extracted for use. All ores are minerals, but all minerals are not necessarily ores.
Rocks- A rock is made up of 2 or more minerals. You need minerals to make rocks, but you don't need rocks to make minerals. All rocks are made of minerals.
Minerals- A mineral is composed of the same substance throughout. There are about 3000 different minerals in the world. Minerals are made of chemicals - either a single chemical or a combination of chemicals.There are 103 known chemical elements. Minerals are sorted into 8 groups.
Difference between rock and mineral - A rock is made up of 2 or more minerals, whereas a mineral is composed of the same substancethroughout.
Ore- A mineral occurring in sufficient quantity and containing enough metal to permit its recovery and extraction at a profit. Or, a mineral or an aggregate of minerals from which a valuable constituent, especially a metal, can be profitably mined or extracted is an ore.
2. What is meant by Geological time scale?
The geologic time scale provides a system of chronologic measurement relating stratigraphy to time that is used by geologists, paleontologists and other earth scientists to describe the timing and relationships between events that have occurred during the history of the Earth. The table of geologic time spans presented here agrees with the dates and nomenclature proposed by the International Commission on Stratigraphy, and uses the standard color codes of the United States Geological Survey.
Evidence from radiometric dating indicates that the Earth is about 4.570 billion years old. The geological or deep time of Earth's past has been organized into various units according to events which took place in each period. Different spans of time on the time scale are usually delimited by major geological or paleontological events, such as mass extinctions. For example, the boundary between the Cretaceous period and the Paleogene period is defined by the Cretaceous–Tertiary extinction event, which marked the demise of the dinosaurs and of many marine species. Older periods which predate the reliable fossil record are defined by absolute age.
Each era on the scale is separated from the next by a major event or change.
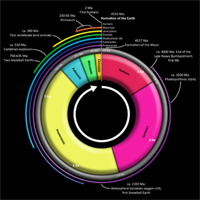 This clock representation shows some of the major units of geological time and definitive events of Earth history. The Hadean eon represents the time before fossil record of life on Earth; its upper boundary is now regarded as 4.0 Ga. Other subdivisions reflect the evolution of life; the Archean and Proterozoic are both eons, the Palaeozoic, Mesozoic and Cenozoic are eras of the Phanerozoic eon. The two million year Quaternary period, the time of recognizable humans, is too small to be visible at this scale.
This clock representation shows some of the major units of geological time and definitive events of Earth history. The Hadean eon represents the time before fossil record of life on Earth; its upper boundary is now regarded as 4.0 Ga. Other subdivisions reflect the evolution of life; the Archean and Proterozoic are both eons, the Palaeozoic, Mesozoic and Cenozoic are eras of the Phanerozoic eon. The two million year Quaternary period, the time of recognizable humans, is too small to be visible at this scale.
3. What is RP, PL, ML & how to get it?
RP means Reconnaissance Permit, PL means Prospecting License, ML means Mining Lease.
Application for reconnaissance permit, prospecting licence or mining lease for major minerals shall be submitted in relevant forms as prescribed in the Mineral Concession Rules, 1960 to the Deputy Commissioner of the concerned district. On receipt of the application and enquiry report from the Deputy Commissioner, the Directorate of Mineral Resources will scrutinize and examine the technical aspects of each case and then forward it along with comments, if any, to the Department of Mining and Geology. The Department of Mining and Geology issues the final grant order followed by deed execution with the Deputy Commissioner, after the concerned individual/firm/company has fulfilled the requisite condition.
4. Explain “PH of waterbodies”
It is the negative logarithm of hydrogen ion concentration and it gives a measure of acidic or basic nature of waterbodies in general or any solvent or solution in question.
5. What is meant by Acid Mine Drainage?
Coal containing significant proportions of pyrites generally on exposure to atmospheric oxygen and bacteria generates sulphuric acid thereby contaminating nearby soil/waterbodies making the latter dead and devoid of life and the acid produced so is called Acid Mine Drainage.
6. Explain the term Geotourism and its scope in Meghalaya?
Huge limestone deposits often results in the development of intricate and beautiful cave systems which in turn results in the development of these caves as Geo-tourism spots.In Meghalaya, there are a number of such geo-tourism spots like Syndai cave, Krem Lymput cave, Siju cave and many more
7. What is the difference between Major & Minor minerals?
Major minerals are those specified in the schedule appended in the MMDR Act,1957 and the common major minerals are Calcite, Clay, Coal, Quartz etc. minor Minerals are those specified in the schedule appended in Minor Mineral concession rules and the common minor minerals are Limestone, Decorative stones etc.
8. How many scholarships are granted every year and what is the amount of scholarship?
Atleast 2/3 scholarships of Rs.400/-pm each are granted every year and a book grant of Rs.1000/-
9. What is qualitative & quantitative chemical analysis?
Qualitative chemical analysis determines the constituent substances whereas quantitative analysis determines the quantity of each constituents present
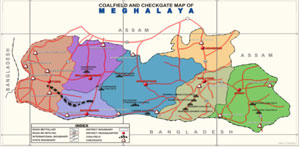
10. What are checkgates meant for and where they are located?
The Department has set up a number of checkgates(15 nos) located on different strategic points/routes in the State for counter checkingthe documents related to payments of royalty/cess from trucks carrying minerals like coal,limestone,quartz etc.Majority of these checkgates are located in and around major coal fields and exit points as shown in the map below:
Checkgates are
- Mookyndur (District East Khasi Hills)
- Dawki (District Jaintia Hills)
- Umkiang (District Jaintia Hills)
- Garampani (District Jaintia Hills)
- Umling (District Ri-Bhoi)
- Athiabari (District West Khasi Hills)
- Borsora (District West Khasi Hills)
- Chorragaon (District West Khasi Hills)
- Dainadubi (District East Garo Hills)
- Gasuapra (District South Garo Hills)
- Daluagre (District West Garo Hills)
- Masangpani (District West Garo Hills)
- Balachanda (District West Garo Hills)
- Boldoka (District West Garo Hills)
- Dadengre (District West Garo Hills)